- Get detailed metrics on API usage, errors, and performance
- Track API adoption and usage by individual consumers
- Log individual API requests, responses, and correlated application logs
- See what’s causing slow API requests with traces
- Monitor uptime and set up custom alerts
Create app
To get started, create a new app in the Apitally dashboard and select as your framework.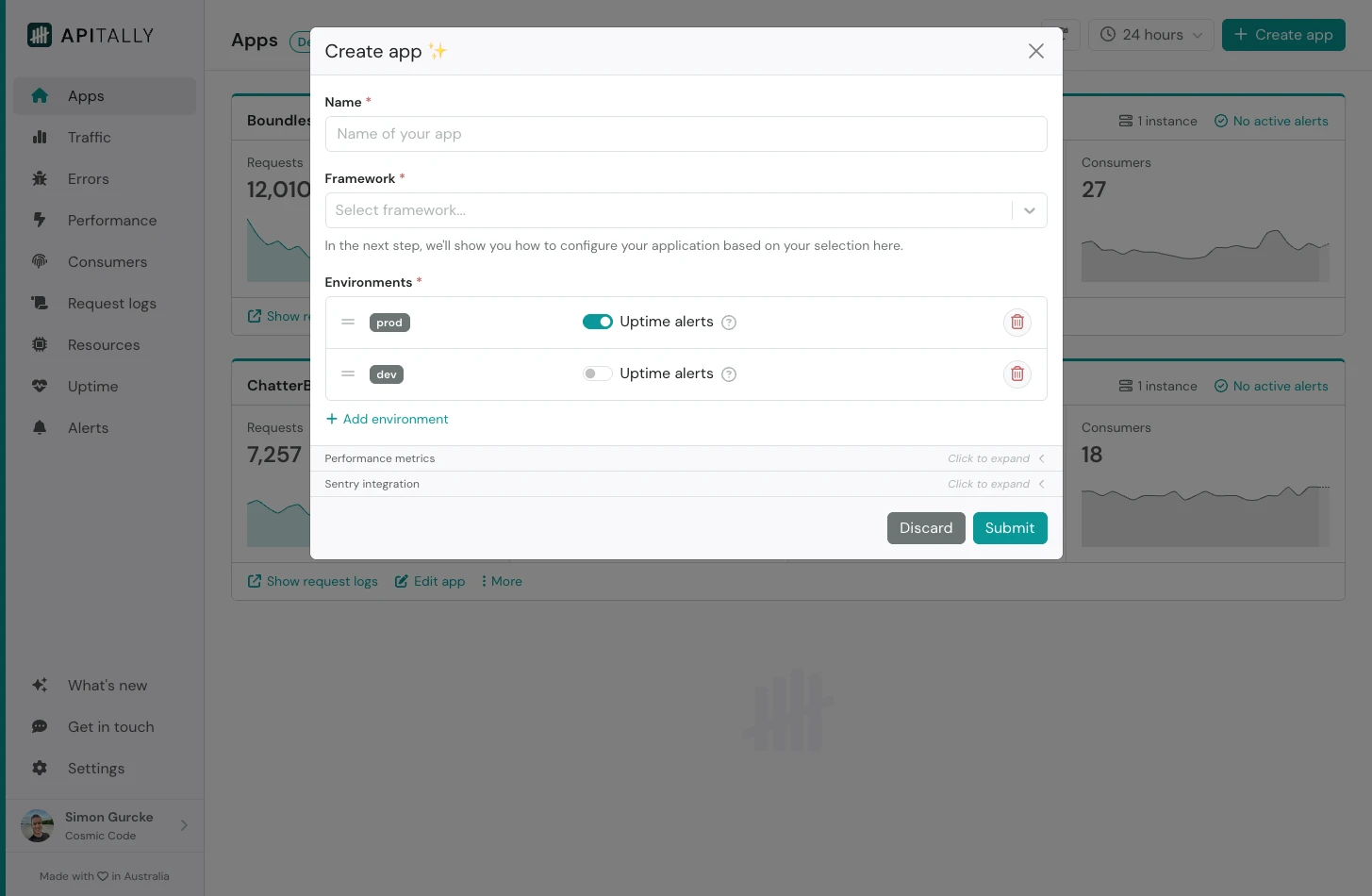 You can also configure the environments (e.g.
You can also configure the environments (e.g. prod and dev) for your app, or simply accept the defaults.
After submitting, you will see tailored setup instructions for your app. These include code snippets you can copy and paste into your project.
The client ID provided in the setup instructions uniquely identifies your app for the purpose of data ingestion only. It does not grant any kind of read access to your data.
Add middleware
Next, install the Apitally SDK in your project with the extra.client_id for your app.
You’ll find the client_id on the Setup instructions page for your app in the Apitally dashboard, which is displayed immediately after creating the app.
If you’re also using other middlewares, add the
ApitallyMiddleware last, so
that it wraps the existing stack of middlewares.At this point the basic setup for your application is complete and you will start seeing data in the Apitally dashboard.
Identify consumers
To analyze and filter API traffic by consumers, you can associate requests with consumer identifiers in your application. In most cases, use the authenticated identity to identify the consumer. The identifier should be a string, such as a username, email address, or any other unique identifier. Optionally, you can also provide a display name and group for each consumer. Use theset_consumer function to associate requests with consumers, for example in a dependency, middleware or directly in your endpoint functions.
The Consumers dashboard now shows all consumers that have made requests to your application. You can also filter other dashboards by consumer.
Configure request logging
Logging of individual requests and responses is disabled by default to protect potentially sensitive data. If you enable it, you can configure in detail what parts of the request and response should be logged. You can also mask sensitive information (e.g. in headers) and exclude certain requests from logging. The SDK applies default masking rules for common sensitive headers, query parameters and request/response body fields.The Request logs dashboard now shows individual requests handled by your application. You can filter, search, and inspect them in detail.
Enable tracing
Tracing gives you a detailed breakdown of time spent during the handling of each request, showing the duration of database queries, HTTP calls, and other operations. To enable tracing, setcapture_traces to True and instrument the libraries you want to trace with OpenTelemetry. See the tracing guide for further instructions.
